[Java] Multi-thread processing
Conclusion
- The difference between processes and threads is important
- The significance of multithreading is that it can be ** run independently and share memory space within the same process **.
What is a thread?
- The smallest unit of processing to execute a program **
- The app runs on a single thread called ** main thread **
- However, with ** single thread **, the application user has to wait for the next operation until the end of communication, such as during network communication.
- If there are multiple threads (= ** multithread **),
network communication will be executed by other threads in the background, and ** processing can be executed in parallel by the main thread even during communication * *
What is a process?
- ** Program instance itself **
- New ** CPU and memory allocation required to start process **
- Process ** has one or more threads **
- 1 to 1..n (1 or more n) relationship
- In UML notation, there are 1… n threads when viewed from the process side.
Process 1 | Thread 1..n
Memory configuration
- ** Process **: Program running on the Main function
- There is a ** thread ** in a large box called a process
- Main function works in 1 thread
- A process must have one or more threads (** main thread **)
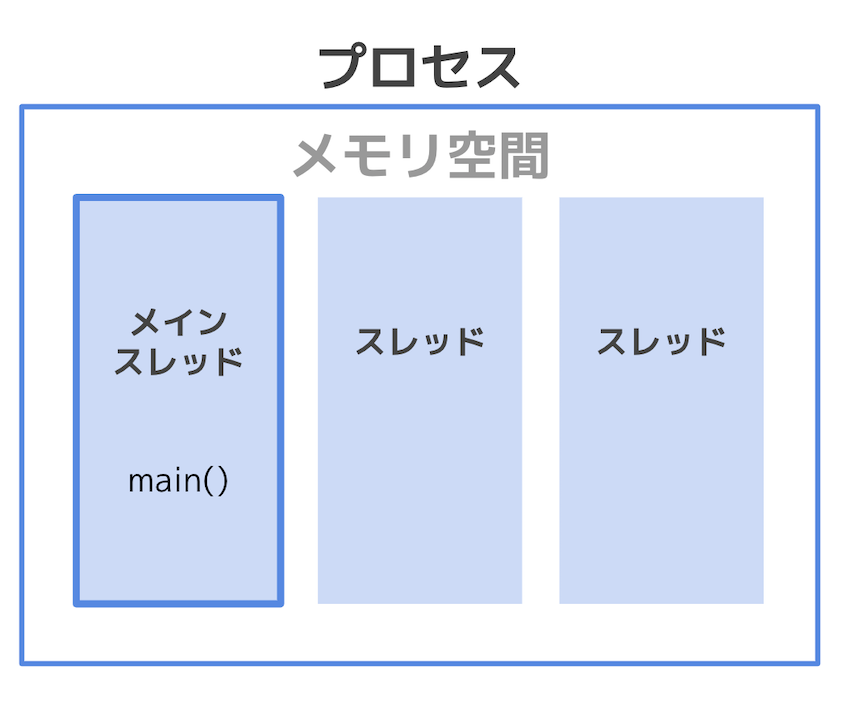
Thread Features-Independent / Memory Space Sharing
- Threads move ** independently of each other **
- Threads that run in the background run independently even if one stops
- If communication processing is performed in the main thread, it will stop while communicating and the answer is returned, so parallel processing is performed to process during that time as well.
- The reason why it is in one process when 3 threads are started with multithreading is ** to share memory space **
- Once the variable is defined in the Main thread ** All threads can access **
public class Main {
String hoge = "hoge"; //This variable is shared
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main().run();
}
private void run(){
while (true) {
System.out.println("1"); //Main thread
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("2");
}
}
}
Thread creation / execution
- Inherit Thread class
- Runnable interface implementation
Inherit Thread class
- Override ** absolute run method (calling endpoint) in Thread derived class **
- Thread derived class methods
- ** currentThread **: Get running thread
- ** getId **: Get thread ID
- ** isAlive **: Thread survival confirmation
- ** join **: Wait ms until thread ends
- ** setPriority **: Priority setting
- ** sleep **: Thread execution pause
public class MyThread extends Thread {
//Thread actual processing is a Thread derived class
@Override
public void run() {
for (var i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
//Get thread name with getName
System.out.println(this.getName() + ": " + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadBasic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Instantiate and create threads
var th1 = new MyThread();
var th2 = new MyThread();
var th3 = new MyThread();
//Start thread with start method
th1.start();
th2.start();
th3.start();
}
}
Runnable interface implementation
- Implementations ** (implements Runnable), not inheritance
- Functional interface
- Since the thread name cannot be accessed directly, get the current thread with the
Thread.currentThread ()static method and access the getName method. - Pass an instance of Runnable implementation class to Thread constructor for instantiation
public class MyRunner implements Runnable {
//Thread actual processing
@Override
public void run() {
for (var i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i);
}
}
}
public class RunnableBasic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Thread creation
var th1 = new Thread(new MyRunner());
var th2 = new Thread(new MyRunner());
var th3 = new Thread(new MyRunner());
//Thread start
th1.start();
th2.start();
th3.start();
}
}
Recommended Posts